A Guide To Achieve Clean Code And Best Coding Practices
Quick Summary: With the help of our in-depth guide on best coding practices, you can write clean Code and improve your programming skills. From meaningful variable names to efficient algorithms, our guide will equip you with the tools to write Code that’s a joy to work with. Uncover expert insights, tips, and techniques that empower you to create software that stands the test of time.
Introduction
As developers, or if you are engaging in software development practices, you will surely understand the weightiness of writing clean Code. And you can also understand the cruciality of knowledge about coding best practices.
However, you must also know how difficult it is to write clean Code all in one go. And how many terms are there to understand to code accurately?
Additionally, as all developers are into different code practices, most of the time, you need clarification about where to get all the knowledge about how to write clean Code, how to solve this issue, Etc.
Hence, you need a complete guide that can cater to your questions and assist you with writing clean Code and best practices.
So, congrats!
You have reached an accurate place where you can not only find a solution, but you can outsource your development project to us as we provide the best software development services.
So, please keep reading and let us know how our best developers can help you!
What is good code and what coding standards are?
In simple words,
- Code that is clean, easy to understand, and follows best coding practices like indentation, commenting, good documentation, etc.
- Which is optimized i.e Written in comparatively less number of lines, No memory leaks, emphasizes code readability and reusability.
- Whose life expectancy is more, which means it is designed in such a way that any modification into it requires less effort.
- That reduces cognitive load (i.e understanding is easy)
- which is concise and to the point.
- Which is fun to write and easy to maintain.
You can consider it clean code. And to achieve this, we apply some rules and follow specific guidelines throughout the project, known as coding standards.
In other words, one should follow these principles, design patterns, and conventions while coding to produce high-quality Code.
There are numerous advantages of utilizing coding standards while developing software
-
- Increases the readability of written source code.
- The entire source code follows the same format and coding style…
- It requires little maintenance.
- Developers’ productivity rises as a result of this.
- Determines the difference between a successful project and, at worst, a project that is dead on arrival
- Reminds you why did you write a certain block of code
- Makes it easy to debug and search for files
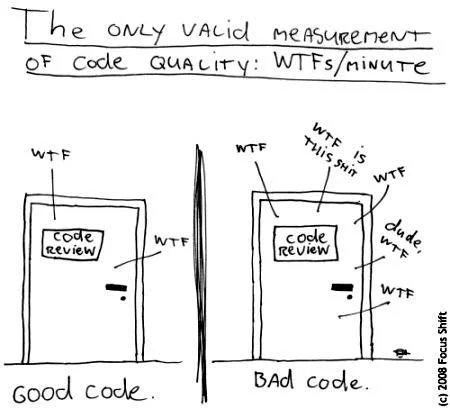
List of best practices for Clean Code And Best Coding Practices
Commenting and Document for Clean Code And Best Coding Practices
- The file should contain- File level Documentation- Author, Description, Name, Modified By, Date should be written on the top of a file.
- Don’t delete the previous person’s code. Comment and write it again with comments.
- Always declare the reason why the method has been made.
- Don’t comment on each line, instead comment for three to four lines.
Code formatting –
- Code formatting improves our readability and transports meaning.
- We should format our code by applying vertical and horizontal formatting
Vertical Formatting
- Like an essay, code should be readable from top to bottom with few jumps.
- Consider separating files containing different concepts (for example, classes).
- Spacing should be used to distinguish different concepts ( e.g function after function, classes after imports. )
- Spacing should not be used to separate similar concepts.
- Concepts that are related should be grouped together.
- Indentation should be consistent throughout the project; select one and stick with it.
Horizontal Formatting
- Lines of code should be readable without scrolling – avoid very long sentences.
- Use Indentation even if not required technically.
- Break long lines into multiple shorter ones.
- Use clear but not unreadably long names for variables, functions.
- Examples
BAD CODE :
let projectMemberInfo = await PROJECT_MEMBER.find
({ user: req.user._id, createdBy: req.user.currentTeam, roles:
{ $in: [ managerRole._id ] }, isActive: { $ne: false },
isDeleted: { $ne: false } },
{ project: 1, _id: 0, project: 1, status: 1, hourlyRate: 1, roles: 1, createdBy: 1 });
GOOD CODE ::
let _query = { user: req.user._id, createdBy: req.user.currentTeam, roles: { $in: [ managerRole._id ] }, isActive: false , isDeleted: false }
let _projection = { project: 1, _id: 0, project: 1, status: 1, hourlyRate: 1, roles: 1, createdBy: 1 })
let projectMemberInfo = await PROJECT_MEMBER.find(_query, _projection);
Naming Conventions
- Names should be meaningful.
- Well-named “things” allows the reader to understand your code without going through it in detail.
- Use the same casing throughout the whole project.
- You can use any of these
- snake_case
- camelCase
- PascalCase
- kebab-case
- Boolean Variables should start with “is”. e.g isValidUser, isOpen, isClosed
- Constant is always Capital, CONNECTION_LIMIT, POOL_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE.
- The first letter of class should start with Caps e.g Account, Storage, RequestBody, Response.
- The function normally starts with verb, e.g sendData(), getData(), fetchUser()
Functions and methods
- At the top of each function, describe it in one or two sentences.
- Calling the function should be readable.
- The number and order of arguments should be clear.
- Function body should be readable.
- The length of the function body matters, an ideal function should not exceed more than 70-80 lines. If it’s exceeding then try to split out the function body according to similar concepts.
- The function should not have nesting of more than 3 loops and if checks.
- Functions should do exactly one thing.
- Try keeping the function pure. ( for the same input function should generate the same output at every time we call. ).
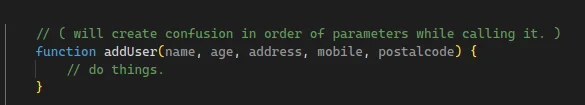
- Try to reduce the number of parameters. If it’s not possible then group them inside a container. (as per my experience while working on a project you don’t want to waste your time on always remembering the sequence and order of parameters. ) (although it’s opinionated person to person.)
-
- BAD FUNCTION PARAMETERS
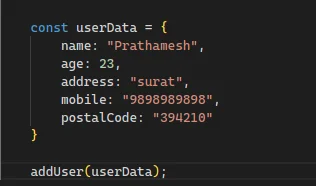
- GOOD FUNCTION PARAMETERS
-
Control Structures and Errors
- Avoid deep nesting of control statements ( loops and if checks )
- Utilize errors
- It’s better to throw errors when they are encountered instead of returning something.
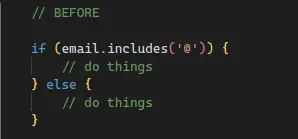
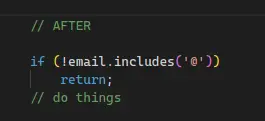
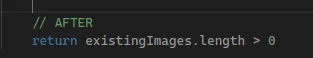
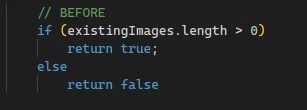
- Use Guards and fail fast.
- e.g
Separation of Code and Refactoring
- Values should not be hardcoded instead use ENUM
- you should typically prefer small classes over a few large classes.
- Every class and method should have a single responsibility
- Classes should be highly cohesive ( How much your class using the class properties. )
- CODE REFACTORING – Changing the structure of code without changing the expected behavior.
- In general, it implies modifying the system to make some of its aspects work more efficiently or use fewer resources or be more robust.

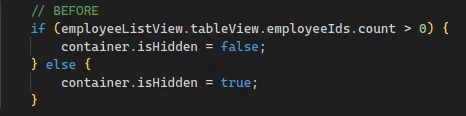
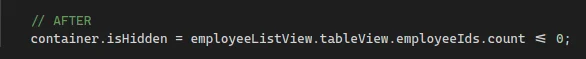
Memory Leaks
- A memory leak is a portion of memory that is no longer utilized or required by an operation but is not returned to the System for whatever reason.
- Avoid using Global Variables.
- Use LifeCycle methods.
- Clear the timeouts and intervals.
- Do not create unnecessary closures.
- Remove event listeners for elements that are removed from DOM.
Programming Principles
USE THE FOLLOWING CODING PRINCIPLE FOR BETTER CODE STRUCTURE
- KISS ( Keep it simple, stupid )
- YAGNI ( You aren’t gonna need it.)
- DRY ( Do not repeat yourself )
- SOLID ( Single Responsibility, Open/ closed, Liskov’s Substitution, Interface Segregation, Dependency Inversion)
- Separation of concern.
- Law of Demeter.
And Design Principles such as Singleton Pattern. Facade Pattern, Observer Pattern, Decorator Pattern, Factory Pattern, Builder Pattern.
Why?
They’ll assist you in developing a clean, modular design that will be simple to test, debug, and manage in the future.
DO’s for (Best Coding Practices)
- focus on analyzing the source code of existing applications.
- Before moving on to the following stage, make sure your documentation is complete.
- Don’t make your standards; instead, follow the ones that have been defined.
- Testing should be followed after changes.
- Make sure your comments are not confusing. Separators and dividers with an unattractive appearance should be avoided.
- Be consistent with file names and directory structure.
- Code Review should be done before production.
- Read open-source code.
- Read about the best coding practices before actually starting to work on new technology.
- Follow the language-specific formatting and best practices guidelines.
- Use Linters e.g pylama for python, eslint for JavaScript & TypeScript, prettier for code formatting.
- Write test cases for checking the code quality.
DON’Ts for (Clean Code)
- Do not create too many global variables.
- Do not use hardcoded values.
- If allocated memory is not being released. Used LIFE CYCLE methods in such cases.
- Lots of commented code.
- Poor Readability.
- Do not write magic numbers.
Conclusion
Although All Above mentioned details and points come from each developer’s experiences in our company, these are the best practices we follow in all our software development work. And we believe it will indeed create a difference between you as a developer and others. However, the above points may be opinionated from person to person. Do let us know your thoughts on this in the comments.
FAQ
What is Clean Code?
Clean coding is a term given to the programming codes that are well structured, clean with proper naming conventions, It underlines the need not only for readability but also for brevity and uniformity in generated software designs. Clean code is clear, leads to less bugs and fewer errors; therefore it is very easy to read, interpret and extend.
How to write Clean Code?
Writing Great code is not only about well-structured code that exhibits good readability and fault-tolerance but also following certain rules or guidelines that enhance your programming experience. First of all, you will work on the choice of the variables that matter and will have descriptive names, and the functions and classes will have meaningful names as well. Try to make your way to the job difficult: use one instructional step and provide a one-line meaning when it’s is necessary.
Break a complex problem down in smaller modules of queries and follow the single responsibility concept. It is always good to use a similar look, Indentation, and whitespace to improve readability. Avoid masked loops and complicated logical operators to ensure the code is easy to understand.
Priority self-documenting Code and style guides or conventions; design pattern; if there is a conflict between your approach and styles,[then] you must adopt a new one. Keep in mind that good Code is an ongoing process that requires first-rate application of quality standards and an effort to delivering consistent, better, codebase.
How to write Clean Code in Java?
When writing code in Java, make it a point to use meaningful and descriptive names for classes, methods, and member variables. The names should adhere to the Java naming standards. Write eye and faith attendants that will be comprehensive and concise. To write more human readable, refactorise the Code and get rid of duplication. At last, assure the test suitability by doing thorough tests with use of frameworks like JUnit and checking code correspondingness and its future changes.







