Combining .NET Backend with Micro Frontends A Modern Approach
Quick Summary:This blog aims to explore how a combination of .NET and micro frontends can provide scalable, modular and future ready application development. It introduces you to the core concepts of key differences from monolithic front ends and why this approach is best for modern enterprise. You will also get to learn benefits, challenges and best practices for adoption of .NET micro frontends.
Introduction
Modern applications these days are not built alone by visualization of today, rather they are built for the future. They must be able to scale, adapt and evolve continuously with the world. Traditional front end architectures have made it hard to manage as features grow and teams expand. Hence this is where combining .NET development services with micro frontend hits the mind.
When you break the user interface into small modules that are independent and self contained, teams can get better flexibility with faster release cycles. As a result, it offers clearer ownership. This strategy, which is supported by security, performance, and long-term support from .NET, enables organizations to update their frontend without compromising stability. It is a balanced approach towards scalable, resilient and future ready applications. Let’s examine the creation of.NET micro frontends in more detail.
What are Micro frontends?
Micro frontends are an approach to the architecture of an application development where the user interface is divided into small, independent and self contained components. Single components further labelled as micro frontends. Hence it basically implies a piece of the user interface which one can develop, test, deploy and scale without affecting the rest of the application.
Instead of .NET micro frontends if you opt for traditional monolithic architecture, complete UI is developed and deployed as a single unit. Rather seeking ideas from microservices architecture and applying it to the front end will allow development of modular, scalable and team oriented applications.
When compared with a monolithic approach, the micro front end has plenty of benefits to offer. Easy maintainability, independent development and deployment, flexibility in terms of technology and enhanced collaboration among teams.
How are Micro frontends different from monolithic approaches?
| Aspect | Micro Frontends | Monolithic Frontend |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | UI is divided into separate, stand-alone parts. | The entire user interface is created as a single, cohesive program. |
| Team Ownership | Multiple teams can work independently on different frontend modules. | One team or tightly coupled teams manage the entire frontend. |
| Deployment | Each frontend module can be deployed independently. | Any change requires redeploying the entire application. |
| Scalability | Scales well for large applications and growing teams. | Becomes harder to scale as the application grows. |
| Technology Flexibility | Different teams can use different frameworks or versions. | Usually limited to a single framework and tech stack. |
| Development Speed | Faster parallel development once the setup is complete. | Slower as the codebase and dependencies increase. |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain individual modules independently. | Maintenance becomes more complex over time. |
| Performance | May introduce overhead due to multiple bundles. | Typically faster initial load with a single bundle. |
| Complexity | Higher architectural and operational complexity. | Simpler to design, build, and manage. |
| Best Use Case | Large products built by distributed teams. | Small to medium applications or early-stage products. |
Understanding .NET framework
The.NET Framework, a software development framework that offers a runtime environment, was created by Microsoft. Moreover it has a set of libraries and tools with which Windows applications may be developed and executed. Although .NET Core (since version 5 called just .NET) is cross-platform, the.NET platform is primarily used on Windows. As a result, a variety of applications, including desktop, web, mobile, cloud, and gaming apps, are compatible with the framework. Its development languages include C#, F# and VB.NET.
Out of the over sixty programming languages that the NET Framework supports, eleven of them were designed and developed by Microsoft. The rest of the non-Microsoft languages are supported by the .NET Framework, which has not been created and developed by Microsoft.
They were platform-dependent by default because they were initially made to run on Windows. Nonetheless, through the use of a cross-platform framework, Mono, and.NET Core, developers are now able to execute.NET programs on Linux, MacOS, and even mobile operating systems.
Scale Smarter with Micro Frontends
- Expert .NET architecture
- Faster, reliable delivery
Why should I opt for .NET Micro frontends?
.NET Micro frontends are the best choice for teams that look to achieve real independence. It helps them ensure that each part of the UI is developed, versioned and deployed separately. Additionally before you make sure to adopt this approach you must gain knowledge on expenditure and ensure that it aligns with the team’s scale and goals.
Version mismatch is one of the most frequent problems that consumers encounter. Compatibility issues might occur when different parts of the application’s UI relies on shared .NET software development or JavaScript libraries. Independent deployments may also result in runtime failures in case host level alters in routing, orchestration or shared contacts are not compatible backwards.
If you feel Microsoft frontends are necessary and the optimal choice for your .NET application make sure you rely on well defined architecture. Employ clear contracts, strict versioning, shared library governance and deployment strategies that avoid breaking changes. .NET Micro frontends can scale well without compromising stability if the proper safeguards are in place.
Benefits of .NET Micro Frontends
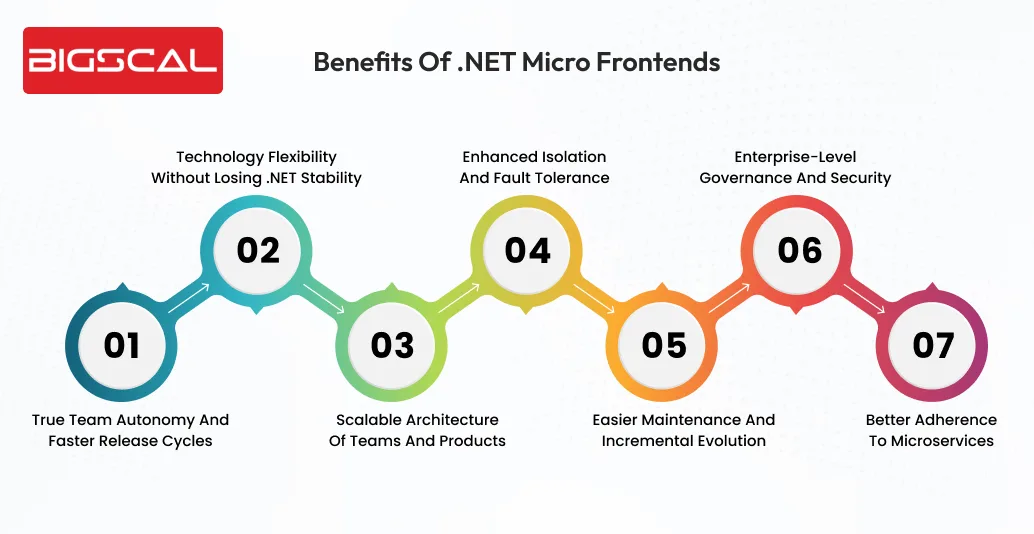
You might be clear about Micro frontends by now and when you should opt for them. So let’s explore benefits of .NET micro frontends for better adoption:
True Team Autonomy and Faster Release Cycles
Thanks to.NET micro frontends, teams can own specific UI parts. It includes their development and testing, their deployment and maintenance. Rather than having one tightly coupled, tightly integrated frontend codebase, each team can focus on a distinct, well-delimited UI domain, e.g. authentication, dashboards, payments or reports.
To this division, teams may be functional simultaneously without causing a hitch to each other. Hence delay in release is reduced significantly since modification in a single micro frontend does not require co-ordination of the whole frontend group. Also independent deployment enables the teams to react to the customer feedback without a full program release, ship more frequently, and correct mistakes faster. This autonomy results in high output and faster innovation to the growing companies.
Technology Flexibility Without Losing .NET Stability
One of the key advantages of .NET micro frontends is the possibility to integrate with various technologies within a stable and well supported environment. You can develop these micro front end for .NET application development as Blazor, Razor pages, MVC or even as JavaScript frameworks. It actually depends on the level of expertise and the framework needed.
Rather than making risky total rewrites, this flexibility allows startups and companies to take up new technology bit by bit. Although modern modules are still running on proven solutions, it is possible to come up with new features using modern methods. .NET provides room for errors and corrections due without compromising on reliability and serviceability due to strong tooling and Long Term Support.
Scalable Architecture of Teams and Products
Scalability access present in .NET micro frontends lets organizations looking to expand deal with traffic efficiently. Each micro front end can be scaled independently to meet growing user demands. Expand.heavily used parts horizontally or make it more efficient without interfering with the other parts.
This architecture is organic with respect to teams as additional teams are added. Moreover the new teams can have new microfrontends without disrupting existing workflows. This reduces merge conflicts, reduces dependencies and allows engineering groups to grow without reducing the speed of development.
Enhanced isolation and fault tolerance
When you opt for a monolithic front end a single bug or performance problem can lead to issues in the entire application. While .NET micro frontend can cut down on this problem by making each UI component independent. In case if a single component fails, loads slower or faces a problem the rest of the application can function normally.
Hence this isolation ensures troubleshooting and debugging is easier because they are present in a small codebase. Additionally, it improves the application’s overall resilience by increasing availability and improving user experience. For business specific applications, this level of daily tolerance is very crucial.
Easier Maintenance and Incremental Evolution
With more features, it becomes harder to maintain very large frontends. Micro frontends in.NET make maintenance easier because teams may update, reorganize, or rewrite individual modules without affecting the frontend as a whole.
This facilitates the use of incremental changes, including redesign of the UI, performance optimization and updating the library. This approach is a significant reduction in technical debt and future proofing of the application as it is used in conjunction with the regular releases and long-term support promised by.NET.
Enterprise-Level Governance and Security
.NET offers strong inbuilt security features such as secure configuration management, authorization and authentication. These characteristics contribute to making similar security requirements to independently-written user interface components when micro frontends are used.
The teams may be autonomous without violating shared security regulations. This particularly comes in handy with business applications where governance, data security, and compliance become very critical. Micro frontends that are built around.NET have balanced control and flexibility.
Make sure to centralize security at platform level to ensure micro frontends are independent without compromising on compliance.
Better Adherence to Microservices
Backends Micro services based backend architectures and.NET micro frontends go hand in hand. The results of the frontend module being able to communicate with its corresponding backend service are clearer ownership, better separation of concerns and cleaner API contract. The system itself becomes easier to understand, test and scale due to this congruency which also reduces cross-team dependencies. Hence you get a more modular and application design that provides you better control.
Conclusion
To conclude when you combine .NET backend with micro frontends it provides a modern yet scalable approach for development of complex applications. Hence by dividing UI into small modules teams can gain autonomy and enhance deployment cycle. Additionally it can improve .NET maintenance services. This architecture lets you adopt a gradual approach for adoption of latest technologies without affecting existing systems. Additionally you can also gain benefits from in-built security provided by .NET framework and its long term support.
Although micro frontends have additional architecture complexity and require constant governance, you can use version control and clear contracts to seek long term advantages. For organizations that are constantly growing or enterprise applications, .NET micro frontends provide flexibility, resilience and foundation that is future proof.
FAQ
Can .NET be used with micro frontends?
Yes, .NET works well with micro frontends and supports UI models built using Blazor, Razor Pages, MVC, or JavaScript frameworks.
What are .NET micro frontends?
.NET micro frontends split the UI into smaller, independently deployable components while using .NET as the backend.
How are micro frontends different from monolithic frontends?
Micro frontends allow independent development and deployment, whereas monolithic frontends are built and released as a single unit.
Are .NET micro frontends suitable for large applications?
Absolutely. They are ideal for large-scale, complex applications that require multiple teams and frequent updates.
Do micro frontends affect application performance?
Micro frontends can introduce slight overhead, but with proper optimization, performance remains stable and scalable.
Can different teams use different technologies in .NET micro frontends?
Yes, different teams can use various front-end frameworks while still relying on .NET as the backend.
Is independent deployment possible with .NET micro frontends?
Yes, each .NET micro frontend can be deployed independently without impacting the entire application.
Are .NET micro frontends secure?
Yes, they benefit from .NET’s built-in security features such as authentication, authorization, and secure configuration.
Do micro frontends work well with microservices?
Yes, micro frontends align naturally with microservices by pairing front-end modules with dedicated backend services.
Are .NET micro frontends future-proof?
Yes, they support incremental upgrades and long-term evolution without requiring major rewrites.





