Introducing Airbrake With Node Js Explained
Quick Summary: If you’re looking for a way to improve your Node.js development workflow, consider using Airbrake Node.Js. This article will briefly overview Airbrake and how it can help you track and fix errors in your Node.js applications.
Introduction
Are you tired of sifting through endless lines of code, searching for elusive bugs that appear out of nowhere? Look no further than Airbrake Node.Js!
Airbrake is the solution to your Node.js error tracking needs. Say goodbye to the frustration of debugging in the dark. With Airbrake, you’ll gain unparalleled insight into the health of your Node.js applications.
Read on to know more about becoming a top-notch node js service!
Airbrake Overview
First of all, you need to Hire Node.Js developers to use Airbrake.
- The official Airbrake notifier for detecting JavaScript errors in Node.js and reporting them to Airbrake.
- Airbrake is available for every language and framework.
- Installed in a minute and takes less time and tracks problems and more time progressed
Why Use Airbrake
1. Developer-centric
Airbrake onboarding is “very easy” for large languages and frameworks. Integration makes Airbrake error monitoring easier, more common, and more useful for developers.
2. Lightweight
A non-standard and non-server design means low maintenance and almost zero technical debt to get the full visibility of every app stack.
3. Immediate Impact
Real-time notifications will get the current effect.
Once Airbrake is installed, you will know more about the current state of your app. Real-time notifications will notify you of new issues and critical errors.
Features of Airbrake
- Simple and fast installation options including npm and yarn.
- Post undetected errors to Airbrake or manually use try/catch.
- Add parameters to your errors for more context.
- Control which errors you send with custom filtering options.
- Easily monitor errors and performance.
- A new error in your code will be notified to you by email or messaging.
- Detect the exact event which caused an error so you can understand the issue and resolve it.
- Airbrake uses protocols that protect your code and sensitive data remains untouchable.
Getting started with Airbrake
First, create an account on Airbrake (https://airbrake.io). They will provide you with keys for each application that you want to keep track of.
– Airbrake dashboard looks like this:
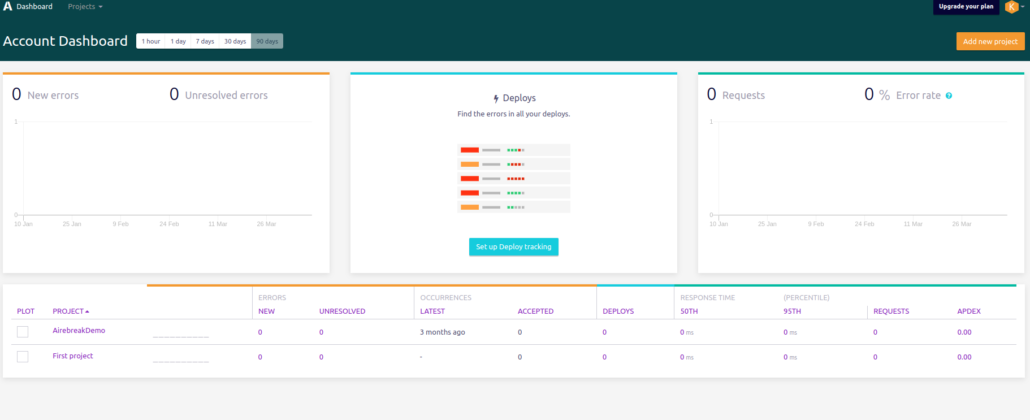
Create a simple Express app using Node.js Application
Install the Airbrake package using the following commands
– Using npm: npm install @airbrake/node
– Using yarn: yarn add @airbrake/node
Now, In the app.js file add the following code after the app variable has been declared
1. Air-brake integration
// Air-brake integration
const airbrake = new Airbrake.Notifier({
projectId: '<YOUR_AIRBRAKE_PROJECT_ID>',
projectKey: '<YOUR_AIRBRAKE_API_KEY>',
});
2. Add middleware before the routes defined
// This middleware should be added before any routes are defined
app.use(airbrakeExpress.makeMiddleware(airbrake));
3. Add error handler middleware for Airbrake
// The error handler middleware for Airbrake
app.use(airbrakeExpress.makeErrorHandler(airbrake));
4. Final app.js looks like this:
var createError = require('http-errors');
var express = require('express');
var path = require('path');
var cookieParser = require('cookie-parser');
var logger = require('morgan');
const Airbrake = require('@airbrake/node');
const airbrakeExpress = require('@airbrake/node/dist/instrumentation/express');
var indexRouter = require('./routes/index');
var scheduleRouter = require('./routes/scheduler');
var app = express();
// view engine setup
app.set('views', path.join(__dirname, 'views'));
app.set('view engine', 'pug');
app.use(logger('dev'));
app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use(cookieParser());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
// Air-brake integration
const airbrake = new Airbrake.Notifier({
projectId: '<YOUR_AIRBRAKE_PROJECT_ID>',
projectKey: '<YOUR_AIRBRAKE_API_KEY>',
});
// This middleware should be added before any routes are defined
app.use(airbrakeExpress.makeMiddleware(airbrake));
app.use('/', indexRouter);
app.use('/scheduler', scheduleRouter);
// The error handler middleware for Airbrake
app.use(airbrakeExpress.makeErrorHandler(airbrake));
module.exports = app;
Setup/Add created project to Airbrake
– After adding this project to Airbrake you can see the project here
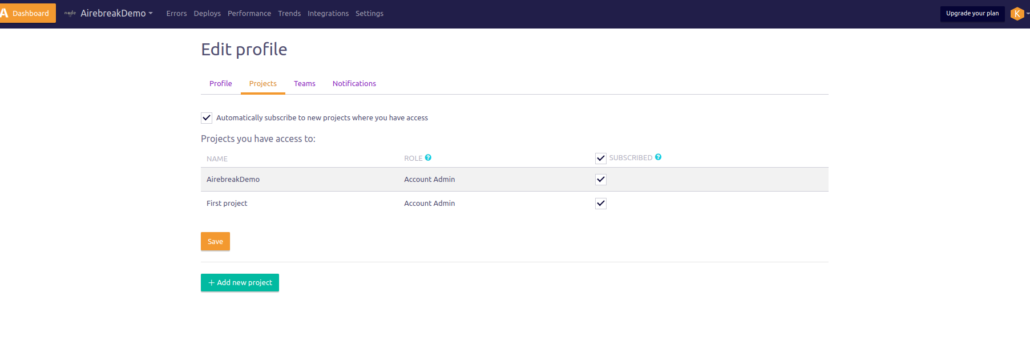
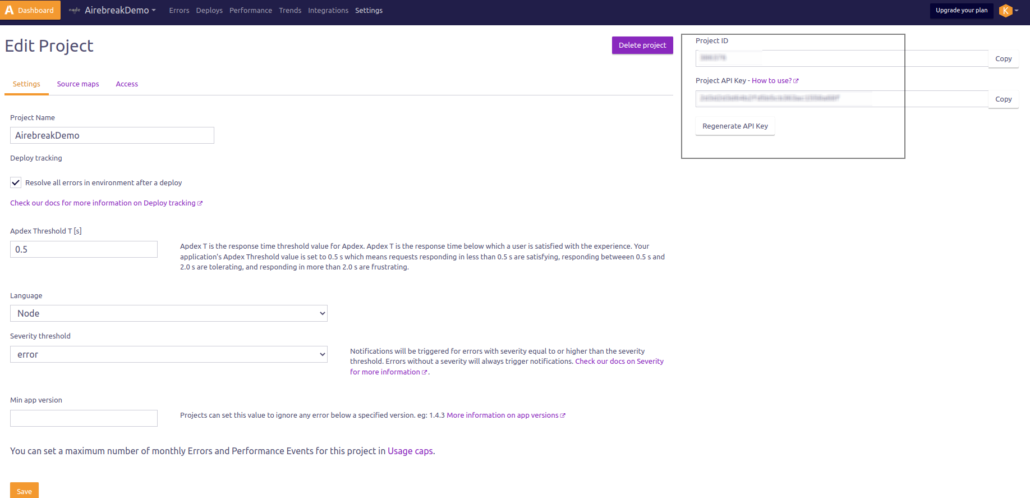
– You can get the project Id and project key by clicking on the project setting. Paste the keys to your code.
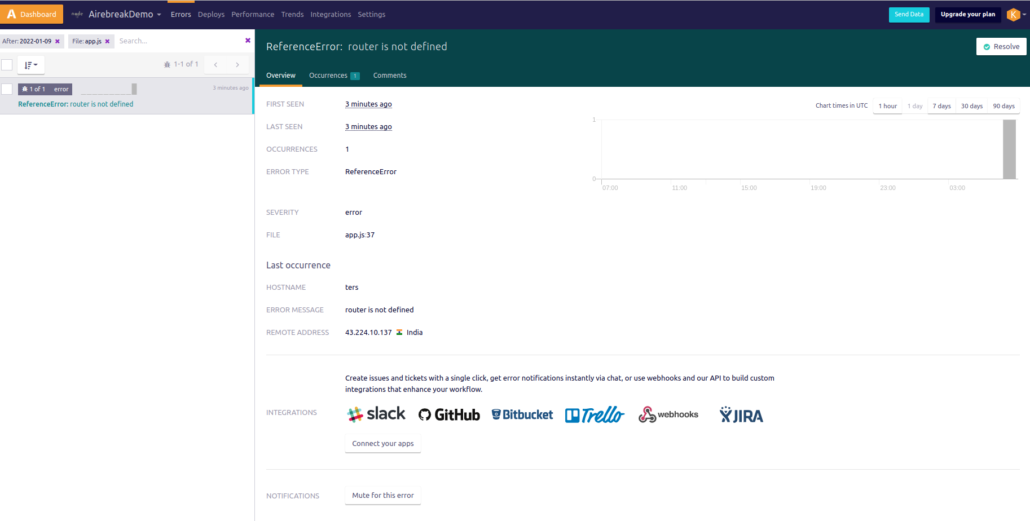
Now if any error occurs in the code it will be shown on Airbrake.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, you have read the immense benefits of incorporating Airbrake into your development toolkit.
Bigscal complements Airbrake by offering powerful error analytics and insights. It allows you to dive deeper into the root causes of issues, helping you make data-driven decisions to enhance your application’s stability and user experience.
So, if you are curious to utilize Airbrake approach Bigscal technologies today.
FAQ
Airbrake vs jake brake?
Citation and Jake are used when it comes to different things. Airbrake could stand for the error tracking and monitoring system which is empowered with a feature of pinpointing and reporting of software problems. On the other hand, Jake brake can be taken as an old-fashioned brake with no software alternative. In the field of software development, Airbrake is a lightweight tool that performs bug tracking and error monitoring.
Are airbrakes better?
Airbrakes can imply various modalities of error monitoring and reporting tools; Airbrake is the example of tracking their deployments across all the environments and users for defining errors’ impacts and prioritizing fixes. io. They can be perceived as an important tool for software troubleshooting and problem solving which tend to be done quicker and more efficiently.
Node.js troubleshooting?
Troubleshooting Node. in js, there is a tendency of seeing problems in the web server, which is called Node and then determining the problem and solving it. js applications. It’s very usual to do the simple steps like the syntax double-checking and the debugging with tools like Node, for instance.
What is exception monitoring?
One of the software development techniques is a concept of exception monitoring and this system monitors the exceptions or errors that occur within the application in a continuous way. It employs various tools and systems for the purpose of tracking.
What is airtable node js
Airtable Node. js can be defined as a form of expressing code using Node. For instance, programming language like js, a JavaScript runtime, is the key to interact with the Airtable API. Airtable is cloud-based database platform which comes with functionality of development of data structures including





