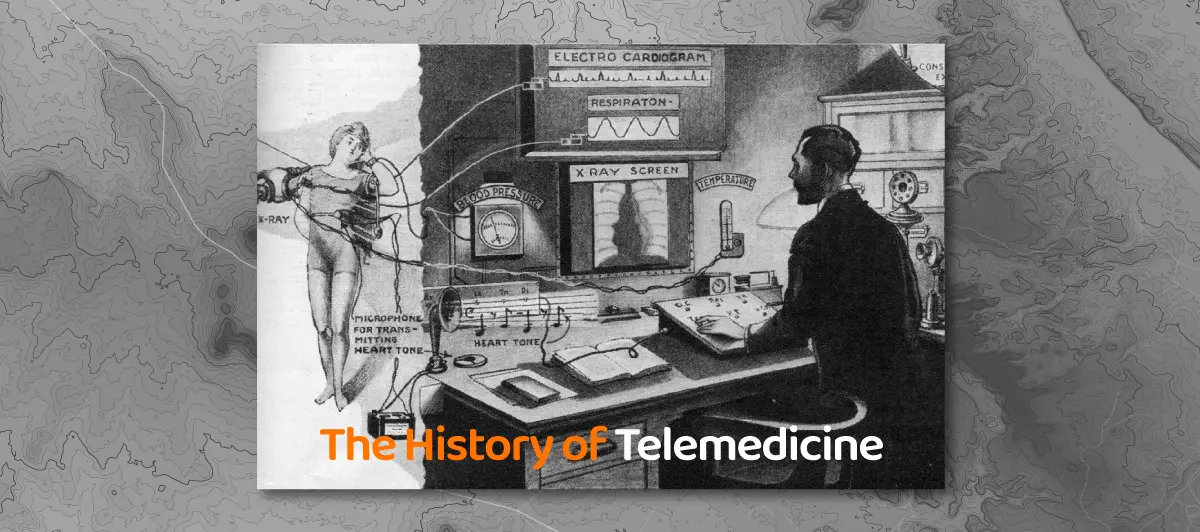
When was Telemedicine Invented? History of Telemedicine
Quick Summary: Interested to gain an idea of when telemedicine was invented? It was invented in the mid-20th century, with its initial roots dating back to the 1960s . It was when remote medical consultations and data transmission began to take shape, marking a significant advancement in healthcare delivery.
Introduction
These days, no person is unaware of Telemedicine. It has certainly been taking over the healthcare industry lately. The benefits of telehealth services no longer seem to be a hidden fact.
Exposure to the latest technological advancements and communication systems is adding to the popularity of virtual health. Although it is a straightforward concept to everyone, many still have a question: When was Telemedicine invented? Many are still surprised to know that it has existed for centuries.
Moreover, the history of telehealth technologies and their recent popularity are due to increased interest in on-demand healthcare services. The main aim of this health technology is to treat patients and communicate data over long distances. People have probably been using this for a long time. Are you curious to know when telemedicine was invented? Keep reading.
What is Telemedicine?
The introduction of modern technology in the world has led to the widespread adoption of telemedicine services in the healthcare sector, irrespective of the practice size. Hence,
Telemedicine isn’t a relatively new term in medical schools.
To simplify Telemedicine, it is about delivering remote clinical services using telecommunications technology. But how is telehealth used in healthcare? It assists health administration in providing affordable and convenient medical care to patients by medical professionals. Moreover, it saves time, reduces costs, and enhances the efficiency of the health system.
Telehealth has been provided through software or application. These software assist to modify clinical infrastructure and expand medical services. Provided instant prescription without traveling that minimizes client costs and preserves enormous time. Moreover, Clients can select their preferable mode of communication and enhance patient centered care.
These remote healthcare services ensure patients don’t miss any other physical exam, examination or examinations through webcam. Hence, medical facilities can be provided through real-time interaction.
Telemedicine consists of reimbursement policies, legalities, and developing a relationship between caregiver and taker. It makes use of technological advancements like mobile devices and digital health resources.
Having a closer look at Telemedicine statistically, it has grown by leaps and bounds. Telehealth technology has plenty of benefits, in general, to offer for both medical students and care seekers.
As per data from Advanced Data Systems Corporation, here are a few statistics to take note of:
- About 50 percent of healthcare organizations in the United States provide telemedicine services.
- The adoption rates are higher in Alaska, Arkansas, and South Dakota.
- About 800,000 telemedicine consultations took place in the US in 2015.
- Additionally, the global market of Telemedicine was at $17.8 billion.
- The demand for telehealth services might keep growing at 18.4% each year.
- More than 70% of people prefer remote consultation over face-to-face visit.
Types of Telemedicine
Remote patient monitoring
Telemedicine facilitates nurse practitioners with remote patient monitoring that helps them monitor patients and keep track of patients with chronic illnesses such as diabetes and blood pressure. Remote monitoring helps rural communities provide healthcare professionals with electronic health record data for review.
Hence, one can conduct primary care visits that can be performed through remote communication and technologies. RPM makes dealing with chronic diseases or at-risk patients easier without going to a hospital or clinic.
Remote monitoring imitates clinic physical exams and depends on tracking tools and electronic health records. These tools assist health care professionals in monitoring health and receiving data effectively.
Hence, it facilitates remote patient monitoring and is an incredible help to providers. It further reduces readmission to hospitals and enhances patient-provider relationships.
Examples of RPM telemedicine tools:
- Glucose tracking devices
- Wearable devices for tracking fitness levels
- Smart beds help monitor patients’ health, get in touch with hospital devices, and make necessary changes for health outcomes.
- Sensors that keep track of the gait and balance of people
Store-and-forward Telemedicine
Store and forward telemedicine solutions, also referred to as asynchronous telemedicine solutions, help providers store and forward medical data. This type of solution should be secure, private, and HIPAA compliant.
It helps providers patients to seek the same level of convenience in person visit that patients desire with real-time treatment. Hence, rather than going through a tedious process for sharing patient data, a doctor can send patient preference emails with related data during diagnosis.
Asynchronous Telemedicine helps in improving clinical communication and patient outcomes. Everyone in the healthcare delivery system, such as patients, providers, and physicians, can share and receive information. There is no need to stay in the same room to continue the treatment process.
Examples of store-and-forward telemedicine:
- Radio doctor uses teleradiology solutions to transmit X-rays to another radiologist
- Teledermatology solutions can help in sending photos for remote diagnosis
- Telepsychiatry enable remote behavioral health treatment
Real-time telehealth
Just like asynchronous Telemedicine, Real-time digital health is known as synchronous Telemedicine. It helps in establishing communication between physician and patient. This communication takes place via video or audio and replaces in-person visits. One can conduct it from the comfort zone of the patient’s home. Synchronous Telemedicine refers specifically to video conferencing or audio communication through HIPAA-compliant platforms. Telemedicine refers specifically to video conferencing or audio communication through HIPAA-compliant platforms.
Synchronous Telemedicine helps both parties quickly and conveniently provide treatment, but it intends to replace in-person visits partially. It enables consultations, recommendations, and patient monitoring. Instead, it plans to be an add-on service for people in rural areas with less access.
Examples of real-time Telemedicine:
- Live video and audio conferencing
- Emergency virtual consultations
- Remote follow-up visits
Evolution of Telemedicine: When was Telemedicine Invented?
To answer your question, when was telemedicine invented? It is not a newer term to medical healthcare professionals and industry. It has existed in different forms since the 1950s, per specific data.
Many professional health-related education universities and hospitals use telephones to share electronic information and electronic health records, consult patients, and share images across geographical boundaries. In 1925, a cool concept like teledactyl came through Inventor Hugo Gernsback. He envisioned offering video game-like controllers to assess patients remotely.
The main goal of Telemedicine was to connect with patients who reside in rural areas and deliver best-in-class medical care, as if they were physically present in a full medical care facility. eVisit was the developer of a patient engagement platform in the 1960s. At that time, the US government channeled lots of money into public healthcare services and innovation.
Telemedicine helps deliver health care services to areas with scarce access to other medical health care, services or equipment. Hence, Telemedicine has, over the years, grown to be a tool for convenience for everyone.
The adoption rate of virtual health has increased because of constant developments in intelligent and personal medical devices. Adoption got faster after COVID-19 pandemic. Patients feel empowered these days to take charge of their health. They can track their health data all through their smart devices.
They can even communicate with their doctors through HIPAA compliance software. Therefore, who would like to waste time traveling in a waiting room when you can do it from home?
History of telehealth and Telemedicine
Ancient Telemedicine
Curious when telemedicine was invented and how did it all start? During its inception, Telemedicine was at an essential stage in places like Greece and Rome around 500 BC. At this time, there were no communication technologies.
Hence, human messengers kept on transferring necessary medical supplies and advice. Additionally, indicators like smoke signals and light reflections helped in communicating information. These signals indicated events like any major disease outbreak or birth.
Early Telemedicine

These inventions were the converting points of long-distance communication, information delivery acceleration and democratized the access of masses to the sphere of broadcasting at a great scale. Because of that, during the Civil War, they provided a great outservice with the ordering of medical supplies and the speedy transmitting of casualties information on the fields.
Things started back in the 1940s in Pennsylvania when officials could take images of the examination center by phone to interact with the specialist who was not nearby. This groundbreaking event is likely the world’s first electronic medical record transfer example.
Building upon this, a Canadian doctor in the 1950s expanded this concept into a teleradiology system. In 1959, the University of Nebraska established a two-way television system to disseminate medical information to students, later connecting it to a state hospital for video consultations.
Moreover, in 1967, the University of Miami School of Medicine collaborated with the local fire department to transmit ECG rhythms over the radio to Jackson Memorial Hospital in rescue situations.
As telephones became ubiquitous, physicians could offer medical guidance to their patients over the phone and consult with fellow medical professionals, to exchange vital information. While modern communication methods may overshadow the significance of telephones today, they undeniably played a fundamental role in the evolution of Telemedicine.
Latest Telemedicine We Know Today

The telemedicine is said to be developed by combining audio and video with real-time data transfer that can be used to provide consultations, continuous monitoring, and various instructions. The start of advanced Telemedicine, as we can paraphrase it today, took place, on the other hand, in the 1960s, which was characterized by great innovations in the area of transmission of medical information, like x-rays and video.
The first case of using this platform in 1959 was again by University of Nebraska personnel who were able to deliver medical services using video communication. This made it possible to grasp the outcome of the brain examination over the air and to break through the communication barrier among the participants in this domain later, for the first time.
The idea of telemedicine solutions in hospital settings can be marked as one of the revolutionizing factors through a pioneering space technology project, known as Space Technology Applied to Rural Papago Advanced Health Care (STARPAHC). The innovative project projected a consortium of healthcare practitioners to provide the astronauts during its Apollo Missions. The Native Americans from the Papago Reservation in Arizona, and onwards, were the recipients of Telemedicine services that employed the same cutting-edge technology used by astronauts during space missions.
The STARPHAC project, thus, is considered as the beginning of a movement of Telemedicine that kept on giving flame to the community for years ahead. Hospitals, medical centers, research institutes; all of them have been prompt to contribute to the field, building up revolutionary and bold projects which led to a very fast ,fickle development of Telemedicine.
How can Bigscal Help in Telemedicine App Development?
Bigscal, the innovator at the forefront of Telemedicine App Development, transfigures the healthcare sector. Given the experience we have in developing the most secure and user-friendly telemedicine technology and clinical applications which, in addition to facilitating virtual doctor-patient interaction, ensures safe remote monitoring, we are best placed in this field now.
Bigscal the application of AI to draw data insights that are guaranteed to be correct and specific care plans recommended. Major Expertise to build medical software and applications and they have in-house medical products that can be customized based on the individual requirements. Furthermore, they run a company for more than 12 years and work on diverse sector projects on a global level. We use an agile development approach to enhance coordination.
They pay attention to healthcare guidelines, ensuring the security of protected health information and are HIPAA compliance while apart from others. They specialize in the development of telemedicine solutions that no longer bind the patient to a specific location and allow them to consult specialists anywhere in the world. While our telemedicine solutions aim to address these underlying inequalities, the outcome also impacts the overall health of the population. Such means their governance is driven by the ability to rapidly deploy onto the changing health needs as well.
Bigscal isn’t just a development partner; they’re the bridge between modern technology and accessible, quality healthcare, reshaping the future of Telemedicine.
Conclusion
Telehealth and Telemedicine represent organic progressions within the healthcare sector, driven by the rapid advancement of telecommunications technologies, mobile technology, and online communication. The healthcare industry mirrors trends seen in other sectors as it strives to adapt to continually shifting regulations and evolving patient expectations in providing care.
These technological breakthroughs, which are shaping and steering Telemedicine, align closely with shifting paradigms in healthcare. They empower healthcare professionals to prioritize patient satisfaction and engagement, underscore the significance of seamless access to clinical services, and emphasize to healthcare software providers the value of affordability and user-friendly solutions. Hope you might have received satisfactory answers to when telemedicine was invented.
FAQ
When was telemedicine invented?
Telemedicine was founded in the middle of the 20th century with reports of the first telehealthcare application, some dating back to the 1960s.
What is the history of telehealth?
Telemedicine which started as a sort of video communication for medical purposes in the 1960’s began its existence. While it might seem somewhat dated now, it has made a nice journey since then.
Why did Telemedicine become popular?
Telemedicine had its boom day as a result of adoption of advanced technologies, which allowed physicians to conduct remote consultations, improve health care accessibility and meet the growing demand for convenient medical services.
When did telemedicine boom?
Telemedicine grew up very quickly in the last few years, the main contribution to this came from more people becoming internet users, the better technologies of real time video communication and the need for remote services during global events like the Covid-19.
What is the difference between telehealth and Telemedicine?
Telehealth is the broad spectrum of all types of remote medical services which are not limited to only healthcare, The term telemedicine is widely used to signify a remote patient clinical management as a consultation or a diagnosis.